

TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Sophia Search Advanced Functionalities
- Upload your own sources to generate text
- Prefilters Usage
- Features Mode
- The Search History
- Limitations and Considerations
Sophia Search Advanced Functionalities
Sophia Search is an AI-powered semantic patent search tool that leverages next-generation natural language processing based on embeddings. It offers advanced AI capabilities for text analysis, enabling the automatic extraction of features. By relying on AI to read and interpret patent documents, Sophia Search can pinpoint which elements or features have already been disclosed in existing patents, streamlining prior art searches and enhancing innovation workflows.
This new search engine is designed to deliver better results through embedding-based technology that enhances recall and precision, while the "Features" mode adds explainability by providing actionable, exportable insights into the relevance of each result.
With an Advanced or Premium subscription, this AI-powered search tool offers the following enhanced functionalities:
- Upload your own sources to generate a synthetic text, that Sophia Search will use to run the search
- Pre-filtering: Allows users to apply filters through the Advanced Search form before launching the analysis, that can significantly reduce the time spent reviewing irrelevant results.
- Features Mode: Automatically extracts features from your input text and uses AI to analyze patent documents, identifying which elements or features have already been disclosed in existing patents.
For details on getting started with Sophia Search and using semantic mode, please refer to the article Sophia Search: AI-powered Semantic Search
For full details on how your information is processed, with or without third-party intervention, please refer to the disclaimer document: AI tools in Orbit Intelligence: Usage disclaimer
Upload your own sources to generate text
You can skip this step if you already have a relevant text, such as a invention disclosure, memo or executive summary etc...
In some situation, you do not have a proper English text to input into Sophia Search. In that case, you can rely on our text generator, based on sources / documents you will upload. Accepted file formats are: Images (.jpg , .png and .webp ), Documents ( .pdf ), and any kind of free text.
First, locate the Add sources button at the bottom left of Sophia Search interface :

A small pop-up will appear and detail if any existing documents are already available for the generation. Now, please use the Add button on the right hand-side

⚠️ If you are uploading an image, a dedicated interface will be shown. You can only upload 1 image at the time, and this image could be associated with an Additional context describing it. This could be seen as an image description for reader of an technical report appendix where the image may be present.
Images without any explanations will produce less relevant output.

You can repeat document uploads until the loader is full. Here an example of sources loader:

As the last step, you can click on the "circular arrows" button to run the text generation. This could take up to 30 seconds, depending of your document's size (in bytes or words). 
The generated text is now ready. Feel free to modify it, remove or add content. Extract Features is most frequent step of this, but you can set up a prefilter or limit to 10 or 50 results (see below).
Nota: if you want another text generation, please modify the uploaded sources (remove/add a document).
Prefilters Usage
Prefilters let you narrow down your search before running it, to improve relevance and efficiency. They are set to limit the initial scope of the semantic search, whereas traditional filters will only filter the output of the semantic search.
After entering your text in Sophia Search interface, you can click on Prefilters Button at the bottom of your window.

This opens the Advanced Search form, where you can refine your search by filtering by date range, jurisdiction, or classification. You can also use keyword suggestions or apply the corporate tree feature to target company-related results.
Once activated, the active Prefilters appear above the input field. You can remove them quickly by clicking the 'X' icon.

Please note that when Prefilters are applied, the maximum number of results is limited to 50.
Features Mode
Sophia Search can extract the 'Features' described in your input. A feature refers to a distinct technical characteristic or component that contributes to the innovation, or a differentiation of the subject matter in the text.
These features act like clues, showing the connection between your query and the document. They can also help to fine-tune your results by simply deselecting any features that aren’t relevant to your search.
⚠️ Features mode uses monthly credits (see section below). 1 credit consumed once you have requested the hitlist.
Automatic Features Extraction and Selection
Click the Extract features button at the bottom of the search window.
A list of detected Features appears on the right side of the window. Review the list and deselect any irrelevant features to fine-tune upcoming search results analysis.
You might consider selecting the three or four most relevant or technically distinctive features. Keep in mind that the more features you choose , the more processing resources and time will be required to complete the text-extraction from each publication.

You can revert to regular Semantic search (without features-extracted - no credit use) by clicking the Clear button located under the features extracted counter (top right).
Features Management
Sophia Search allows users to manage AI-extracted features to customize results analysis.
Users can add, edit, or delete features as needed.
- Adding a new feature:
Click on the "+ New Feature" button located at the top-right corner of the features' list. A pop-up window will open, where you can enter the Title and Description of your new feature.
A pop-up window will open, where you can enter the Title and Description of your new feature.
While editing, tips for writing the description are displayed along with a validation message to help you stay within the optimal or allowed length.
The optimal description length is set to be between 80 and 199 characters.
Saving a feature places it at the top of the list and the new entry is labelled with the “Added” tag.
The maximum number of features remains 10 (AI-extracted or manually added). Once this limit is reached, the New Feature button becomes disabled.
- Editing a feature:
To edit any feature, hover over it and click the Edit icon ✏️ displayed on the right.
A small pop-up window opens where you can edit the Title and Description. Once modified, the “AI-generated” tag is replaced with “Edited”.
- Deleting a feature:⚠️This action permanently removes the feature and cannot be undone. To delete a feature, open the edit modal (by hovering over it and clicking the ✏️ Edit icon) then select the "Delete" button.⚠️ Re‑extracting features is required to restore the original AI‑extracted features list. This action overwrites the current list and manually edited or added features will be lost.
Understanding Credits in Features Mode
- Advanced and Premium users have a monthly credit allocation for using Features mode in Sophia Search. No credit allowed for Essential users.
- Each user receives a fixed number of credits per month, automatically refilled on the 1st of each month. Unused credits do not roll over to the next month.
- Credit allocation by license type:
- Advanced: 20 credits
- Premium: 40 credits
- One credit is consumed each time a search in features mode is successfully executed : search is launched with at least one feature selected and hitlist reached. No credit is consumed by just extracting features.
- The credit system does not applied to Prefilters usage or to Semantic Mode (no features)
The number of remaining credits is displayed at the bottom right of the search interface.
Results Review in Features Mode
After a search with Features mode activated, the Features Match column is added to your hitlist.
Keep in mind that in Features mode, Features match ranking takes priority over Semantic Match ranking. In other words, a result that is less "semantically" relevant (the second for instance) may appear at the top of your hitlist if it is disclosing more features than the most 'semantically' relevant result.
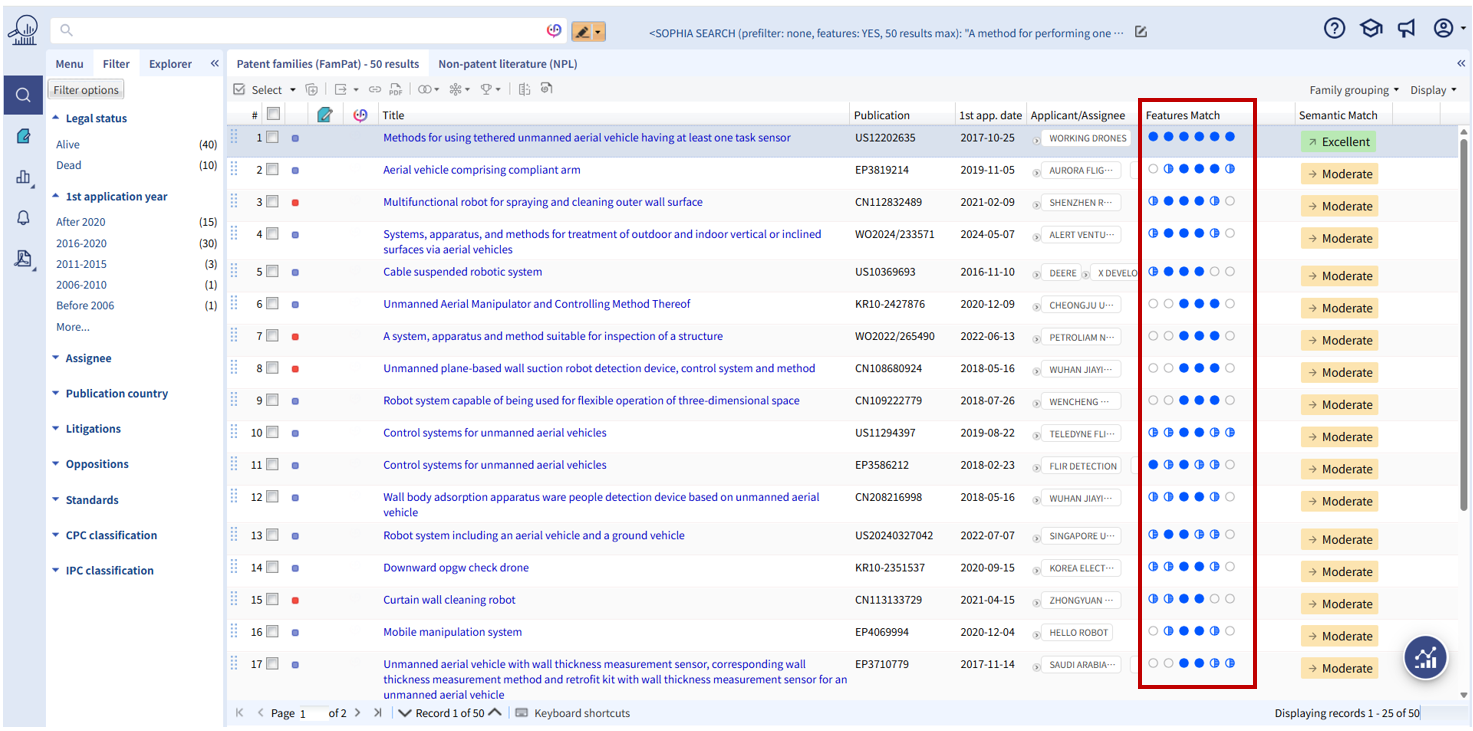
When you hover over a feature match, a tooltip displays its title and description for quick reference.

For more insights on a specific result, you can activate the tab Sophia Search in the right-handed pane from the hitlist, or you can go to the Family View by clicking on the patent family of interest.
✅ Tip: Don’t forget to add the Sophia Search tab to your display for full functionality.
The Sophia Search tab provides detailed information about each feature and the snippets that justify its status.

For each feature, you will find:
- Number, title, and description for easy reference where the disclosure is deemed to be
- Status like disclosed or partially disclosed, displayed clearly after the feature title.

Under each feature disclosed, up to 3 snippets will be shown to substantiate this point:
- You’ll see a snippet number, the Publication stage, and the claim or paragraph number where the snippet was extracted from. Nota: FAMPAT, the publication stage shown is the one used for embedding computation.
- To copy a snippet, hover over it and click the “Copy to clipboard” button that appears to the top right of the snippet.

Additional tools in this tab:
- The menu on the right visually represents the status of all features and serves as a navigation panel to move between features easily.
- You can export all the content of this tab, by using the XLS button at the top right.

One Click report: your prior art report
From the hitlist, when you select up to 10 results, you can instantly generate a prior art report, ready-to-use Excel file.
This export/report is available on the review results page only when Features mode search is used.

This Excel file includes 3 sheets:
- INFO: When, what and which features have been used to generate this export.
- FEATURE_TABLE: For each selected feature, a table will indicate where a possible disclosure is currently available across the different publication stages included in your results.
- DOCUMENT_TABLE: A basic export containing commonly used data such as title, abstract, and permalinks from your selected results in the hitlist.
The Search History
Each executed search is stored in the Search History, including all associated details such as pre‑filters, features, and the input text.

The Search History records how many features were selected, as well as how many were edited or added.
For example: “Features: YES, 5 features selected, including 2 edited/added.”
Users can then reload a previous search directly from the history, restoring the same parameters and tags.
Limitations and Considerations
In this section you can find some technical constraints and behaviours to keep in mind when using Sophia Search.
Sources or documents upload
Your documents will remain stored in our Orbit servers only for the needs of processing by the AI model (see our disclaimer here). Once you have started a search and reached the hitlist, your documents are discarded. There is no medium-term storage, or permanent document library.
Execution Time
Searching with Features mode takes significantly longer than in Semantic mode only, and applying Prefilters may further increase execution time (depending of your keyword-search complexity if any).
Here some average execution times under normal conditions:
- Semantic mode (no Prefilters): 1–5 seconds
- Semantic mode (with Prefilters - truncated words in fulltext): 10–20 seconds
- Features mode (5 Features, 50 results max): 1–2 minutes
Combining Queries
When combining a Sophia Search query in Features mode with another query from the Search History, feature information is lost, and the final result of your strategy will not display any content in the Sophia Search tab.
Usage Responsibility
Responses from Sophia Search must always be verified using your own expertise and the original patent text. They do not constitute legal advice.
Contextual Limitations
The analysis is limited to the text of patent families. Extremely long patents (e.g., 200 pages with dense technical content) may exceed what the LLM can fully process — each model has intrinsic limitations in the amount of text it can handle.
Non-Deterministic Output
Although powerful, LLMs are inherently non-deterministic. The same search request can generate different responses (snippets mainly).
Was this article helpful?
That’s Great!
Thank you for your feedback
Sorry! We couldn't be helpful
Thank you for your feedback
Feedback sent
We appreciate your effort and will try to fix the article